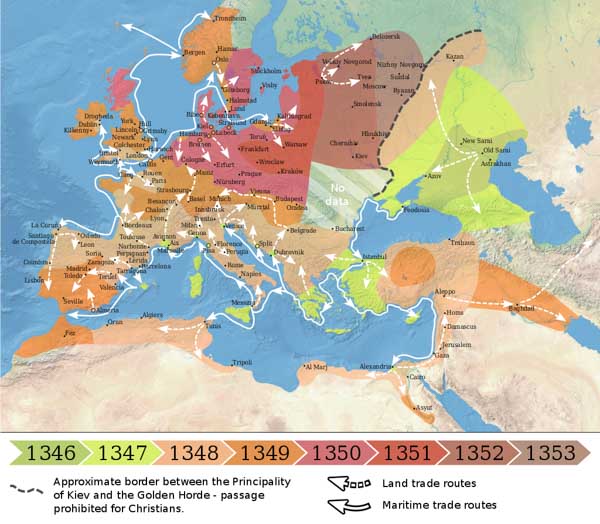
3. Black Death, Plague (1346-1353) Europe, Asia, Africa – 25 million deaths
The bacterium Yersinia pestis, which results in several forms of plague, is believed to have been the cause for the epidemic. The Black Death was the first major European outbreak of plague, and the second plague Pandemic. The plague created a number of religious, social and economic upheavals which had profound effects on the course of European history.
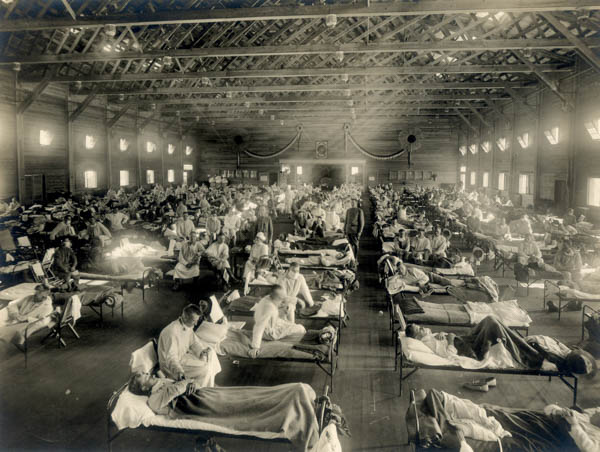
2. Spanish flu (1918-1920) worldwide – over 25 million deaths
The 1918 influenza epidemic, colloquially known as Spanish flu was an unusually deadly influenza epidemic, the first of the two epidemics involving H1N1 influenza virus. It infected 500 million people around the world, including people on remote Pacific islands and in the Arctic.
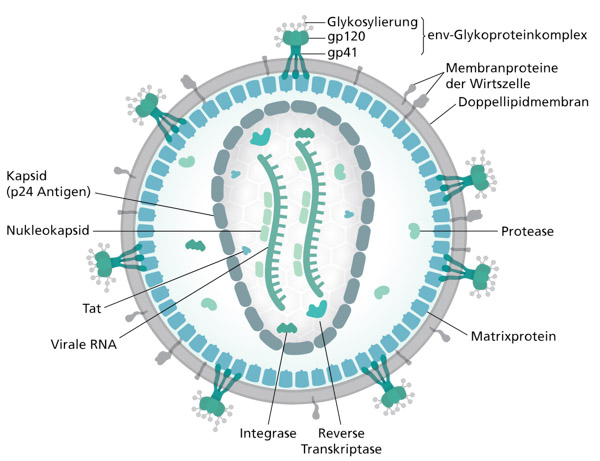
1. HIV (since 1980) worldwide – 36 million deaths
HIV/AIDS is a global epidemic. As of 2017, approximately 36.9 million people are living with HIV globally. In 2018, approximately 43% are women. There were about 940,000 deaths from AIDS in 2017. The 2015 Global Burden of Disease Study, in a report published in The Lancet, estimated that the global incidence of HIV infection peaked in 1997 at 3.3 million per year. Global incidence fell rapidly from 1997 to 2005, to about 2.6 million per year, but remained stable from 2005 to 2015.